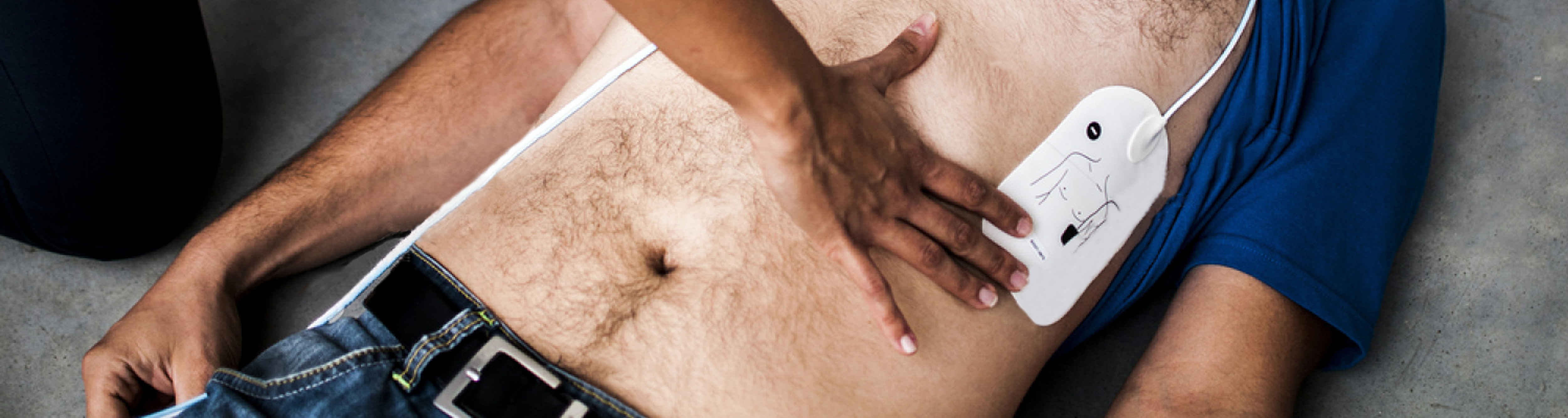
All you need to know on defibrillation electrodes
Defibrillation consists in an electrical current passing through the myocard - the heart muscle tissue - to get it back to its normal rhythm. An essential step in helping a sudden cardiac arrest victim.
As the main accessories of AEDs, defibrillation electrodes have several functions:
- They are the point of contact between the AED and the patient
- They capture and transmit the heart's electrical activity (the ECG tracing), to analyze it and determine shock delivery or not.
- They transmit electrical current through the victim's chest if a shock is recommended by the device.
Defibrillation should be performed quickly after identifying and recognising the Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA).
It is imperative to perform this step in parallel with an early CPR to greatly increase the victim's suvival rate.
Find out all about the Survival Chain for adults and children.
Contained in an airtight package, defibrillation electrodes are self-adhesive and covered with a gel on the side that comes into contact with the skin of the victim to facilitate the electricity passage and minimize burn risks.
Each manufacturer offers electrodes with connectors adapted to a type of defibrillator. They are usually pre-connected to the device in order to save the rescuer a maximum amount of time during the intervention.
Packaged in pairs, defibrillation electrodes are single-use and should be replaced after each use.
Expiration date
Over time, the electrode's conductive gel can dry out, lose some adhesion and no longer ensure optimal contact with the skin.
With an average life of 2 years, it is strongly recommended to regularly check that the expiry date of the electrodes is still valid.
Some pre-connected electrodes are equipped with an RFID tag, to indicate - thanks to an light indictator on the device - if the expiry date has been reached or not. Learn more
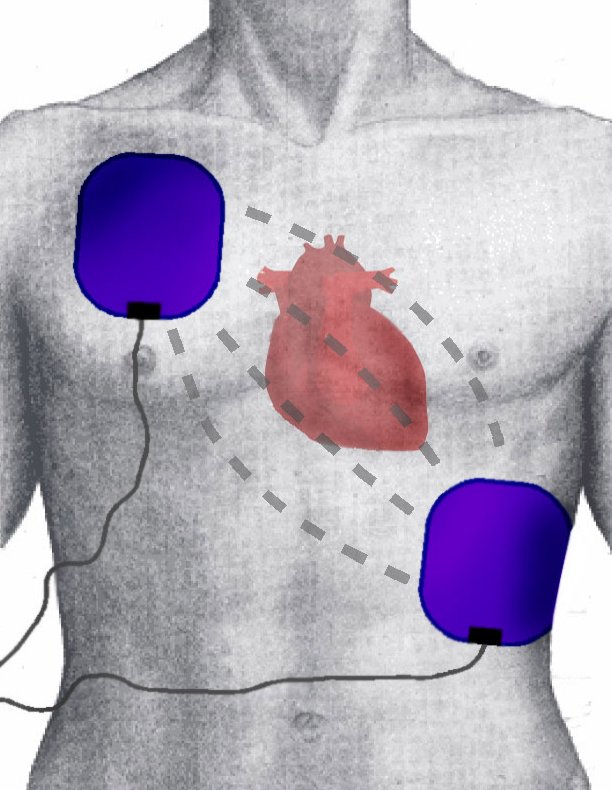
For successful defibrillation, the electricity flow must be from one electrode to another through the chest.
When placing electrodes on the patient, pay attention to sweat, moisture or any other conductive material that may interfere and deflect electricity to the chest rather than into the electrode.
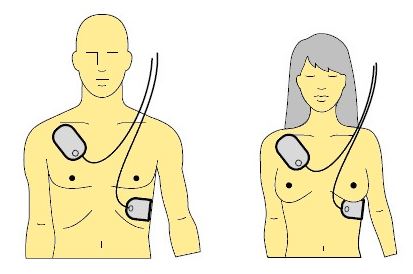
An electrode should be placed under the right collarbone and the second electrode should be placed below the left chest (5-10 cm below the armpit).
Be sure to remove any object that could interfere with the smooth running of the procedure (bra, piercings, jewelry ...).
Pediatric electrodes
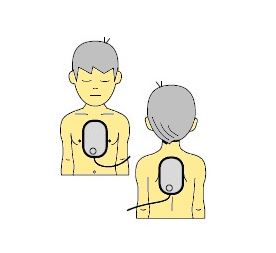
These specific electrodes distribute a suited electric charge to chilidren's size - if they are available, use them. Place an electrode on the child's chest (between the nipples and the sternum), and position the other in the back, between the shoulder blades.
Caution: During an intervention, always follow the instructions on the electrode's packaging and follow the vocal and visual instructions of the defibrillator.
Lors du choix de votre défibrillateur, le type d'électrodes utilisées et un paramètre à ne pas négliger.
Voici quelques conseils à suivre:
- Préférez plutôt un appareil avec des électrodes pré-connectées. Cela constituera un gain de temps notable pour le sauveteur.
- Choisissez un défibrillateur effectuant des auto-tests réguliers. Il pourra alerter par un voyant lumineux l'état des électrodes.
- Optez pour un appareil ayant les électrodes de défibrillation adulte et pédiatrique, pour être prêt dans n'importe quelle situation.